
Global Social Protection Domain API Specification Project
- Industry: Social Protection
- Location: Global
Introduction
In an era where the demands on social protection systems are greater than ever, traditional methods of managing and disbursing assistance have proven to be increasingly inadequate. Bureaucratic inefficiencies, data inaccuracies, and limited accessibility have left countless individuals and families struggling to access the vital support they need.
Working in partnership with an international healthcare consulting company, Tntra contributed to the Digital Convergence Initiative, an open, transparent, and virtual community working to build a global consensus around social protection information systems standards. The initiative is poised to streamline operations and significantly enhance the reach and effectiveness of social security programs globally.
This groundbreaking initiative promises to usher in a new era of social protection worldwide. With seamless integration, real-time data analytics, and a user-centric design, this software technology ensures that assistance is delivered swiftly and accurately to those who need it most. Join us as we delve into how TechSolutions Innovations is poised to reshape the world of social protection systems for the better. Witness the transformation that promises to make a profound difference in countless individuals and families worldwide. Read the case study to explore how this transformative solution promises to transform and make a profound difference in countless individuals and families worldwide.
Business Problem
Fragmentation and lack of communication among social protection programs hinder their full utilization and effectiveness.
The absence of harmonization and interoperability in social protection systems leads to inefficiencies in the utilization of public funds.
Unlike the healthcare sector, which has established interoperability architecture and standards such as OpenHIE 5 and FHIR standards 6, no such standards exist for the social protection sector.
The lack of standardized digital solutions in social protection programs prevents countries from fully realizing technology's benefits in this domain.
Project Goal
- The project aims to establish standardized protocols, data formats, and communication methods specific to the social protection sector.
- It enables seamless data exchange among government agencies, NGOs, and service providers involved in social protection programs.
- The initiative strives to streamline social protection processes, reducing fragmentation and enhancing overall program efficiency.
- By promoting interoperability, the project seeks to optimize the effectiveness of social protection services for the target population.
- Standardizing systems is anticipated to result in cost savings through reduced duplication and improved resource allocation.
- The project strongly emphasizes maintaining data integrity and security to protect sensitive beneficiary information.
Solution
- Tntra began by conducting a comprehensive needs assessment to understand social protection programs' specific requirements, challenges, and goals in different countries and regions. We analyzed the existing systems, processes, and data sources used in social protection programs to determine the extent of fragmentation and interoperability issues.
- Tntra worked with an international healthcare consulting company and involved relevant stakeholders in the design and development process, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, social service providers, and IT experts.
- We created a standardization framework for the social protection sector. The framework encompassed data formats, communication protocols, and security measures similar to the healthcare sector. We also recommend considering existing healthcare interoperability standards (e.g., FHIR) as a starting point and adapting them to the social protection domain.
- The experts at Tntra created a technical specification for APIs that promotes interoperability. It is aimed that these APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and data exchange methods will be endorsed by diverse Digital Public Goods providers.
- We also presented an API blueprint with finalized data entities.
- Our team established precise data standards and objects for recognized entities to address the requirements of various use cases commonly encountered in the social protection domain.
Business Impact
- Interoperability reduces duplication of efforts, streamlines processes, and minimizes the need for manual data entry and reconciliation. This leads to cost savings for government agencies, NGOs, and service providers as they can operate more efficiently.
- By enabling seamless communication and data exchange among different stakeholders, interoperability improves the efficiency of social protection programs. This means quicker response times, reduced administrative overhead, and more timely support to beneficiaries.
- Interoperability allows for better tracking and monitoring of resources. Government agencies can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that funds are directed where needed most, leading to better program outcomes.
- Standardized data exchange ensures that data remains consistent and accurate across systems. This leads to improved data quality, reducing errors and data-related issues that can be costly to rectify.
- Interoperability facilitates easier compliance with regulatory requirements and reporting standards. This reduces the administrative burden associated with compliance and ensures transparency in program operations.
- Interoperability can help identify potential issues early, allowing for proactive risk management. This reduces the likelihood of costly program disruptions or compliance violations.
- Organizations and government agencies demonstrating efficient and effective social protection programs through interoperability can enhance their reputation, attracting more support and funding.
- Properly implemented interoperability standards include security measures to protect sensitive data. This reduces the risk of data breaches and legal liabilities.
Features
Have a look at the top features that our developers incorporated into the solution.
APIs
APIs provide a standardized way for different software applications to communicate with each other. They define the methods and data structures that applications can use to interact. RESTful APIs and SOAP are examples of technologies used for this purpose.
Standards and Specifications
Many industries have established standards and specifications to promote interoperability. For example, HL7 (Health Level Seven) and DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) are used to ensure compatibility between healthcare systems and medical devices.
Security
Systems need to verify the identity of users or other systems and determine what actions they are allowed to perform. Standards like OAuth and OpenID Connect are used for secure authentication and authorization.
Data Mapping and Transformation
When data models differ between systems, mapping, and transformation mechanisms are required to convert data from one format to another. Tools like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are commonly used for this purpose.
Compatibility
Systems should be capable of handling different languages, character sets, and regional preferences to cater to a global user base.
Versioning
Systems may evolve, so mantaining versioning and backward compatibility is important. Latest software versions should still be able to communicate with older versions when necessary.
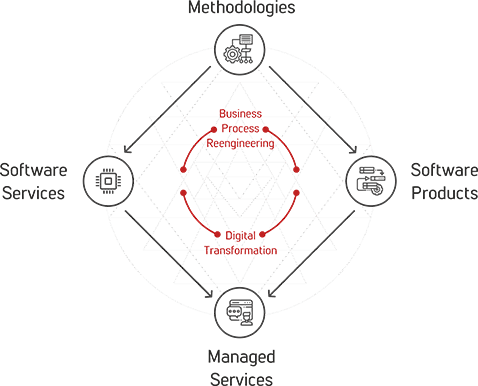
Tntra Diamond
Tntra's Diamond is a comprehensive approach to helping enterprises manage the constant interplay between Business Process Reengineering and Digital Transformation. Tntra’s domain specific methodologies lead to software services for mature systems and software product engineering for new requirements, further transitioning to a managed service model to ensure stability and scale.
Tntra's Diamond enables the enterprise to stay ahead of the transformation curve, while at the same time ensuring optimal business processes to meet the needs of the new economy.


