
CBDCs and Cross-Border Payments: Revolutionizing International Transactions
Table of Contents
ToggleCBDCs have the potential to revolutionize cross-border payments. CBDCs can dramatically cut transaction costs and processing times by eliminating intermediaries. Their underlying technology allows for faster, cheaper, and more transparent transactions. While problems persist, the potential benefits to global trade and financial inclusion are significant. Central banks, financial institutions, and payment networks must work together closely to ensure successful implementation. Continue reading to learn more.
The Bahamas, the first jurisdiction in the world to issue a central bank digital currency (CBDC), is currently drafting legislation requiring commercial banks to allow access to the e-money in order to encourage adoption, according to the country’s central bank governor.
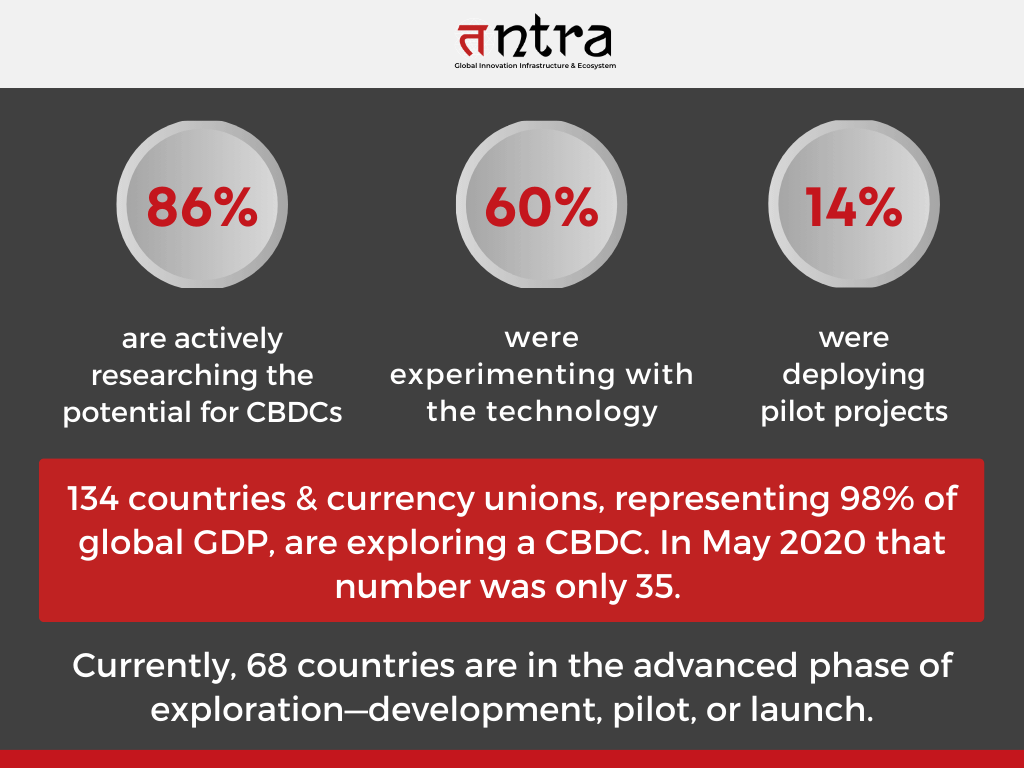
The Bahamas’ reputation as a CBDC pioneer (it introduced its “Sand Dollar” digital currency in 2020) means that what it does in the Caribbean is keenly monitored by the more than 130 countries, ranging from Europe to China, that are currently researching digital versions of their currencies.
CBDC and cross border payments have become a source of controversy between central and commercial banks, with banking lobby organizations warning that the currencies may encourage deposit flight by effectively offering the public a central bank bank account.
The European Central Bank has indicated that if a future digital euro is implemented, it will be required for euro zone retailers and banks to accept and distribute it, but this is still years away, therefore the Bahamas will be first once again.
CBDC cross border payment solutions are available in two forms: the ‘Sand Dollar’s Retail’ version, which the general public can use, and the ‘wholesale’ version, which is only available to financial institutions.
Ordering banks to make the Sand Dollar available would necessitate considerable adjustments to their IT systems, but the Bahamas central bank views it as critical to increasing CBDC acceptance and mobile payments in general. CBDCs have become a source of controversy between central and commercial banks, with banking lobby organizations warning that the currencies may encourage deposit flight by effectively offering the public a central bank bank account.
The European Central Bank has indicated that if a future digital euro is implemented, it will be required for euro zone retailers and banks to accept and distribute it, but this is still years away, implying that the Bahamas will be first again.
(Source: Reuters)
The Ascent of CBDC
As of July 2022, almost 100 CBDCs were in the research or development stage, with two fully operational: the eNaira in Nigeria, which was introduced in October 2021, and the Bahamian sand dollar, which debuted in October 2020.
The value of transactions handled using central bank digital currency, or CBDC, is expected to increase by 260,000 percent between 2023 and 2030. This is according to a market estimate generated in early 2023 using various conditions and sources accessible at the time.
How CBDC will Revolutionize Cross Border Payments
The widespread focus on Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and financial inclusion projects for cross-border payments is primarily motivated by the need to reduce transaction costs through economies of scale and network benefits, as well as to improve cross-border payment efficiency. This has also given rise to a high demand for CBDC-focused software product engineering solutions.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital tokens issued directly by central banks that function similarly to physical cash but exist electronically. The benefits of CBDC for cross border payments are plenty. These tokens have the potential to transform cross-border payments by using speedier processing times and secure digital ledgers. This might eliminate the need for intermediary institutions, lowering transaction fees and delays while increasing transparency and financial inclusion in global trade. CBDCs have the potential to alter cross-border payments in the following ways:
- Eliminate intermediaries
The complexity of cross-border payment technology has forced traditional bank systems to rely on third parties (such as payment networks and credit card firms) to help with the process. These third parties may charge hefty fees for their services in connecting dissimilar payment systems, while potentially gaining access to transaction data. CBDCs enable banks to make cross-border payments without middlemen, allowing them to avoid sharing data with other parties while lowering the cost of cross-border payments for everyone. - Enable interoperability
Interoperability between blockchains and digital currency for international trade is still developing, but CBDC technology can facilitate interoperability across different currencies. Financial institutions and technology providers must learn as they develop and implement pilots. The benefit of digital currency technology is that it allows companies to be more agile when making changes while also giving better governance over such changes. This enables central banks to make much-needed changes throughout the production cycle. - Efficient, affordable & transparent payments
BDCs offer streamlined transactions. They use distributed ledger technology (DLT), which enables real-time processing and settlement, drastically lowering cross-border transfer times. CBDCs have the ability to reduce overall cross-border transaction costs by eliminating intermediary banks and associated fees. This helps both businesses and individuals. CBDC transactions could be based on transparent, immutable ledgers. This creates a clear audit path, minimizes the likelihood of errors, and increases money traceability.
Future of CBDC for Cross Border Payments
The transition to CBDCs is not intended to completely replace SWIFT. Both systems can coexist and possibly compliment one another. Collaboration among central banks, financial institutions, and SWIFT will be critical to ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits of CBDCs for international payments.
CBDCs offer a promising potential to build a faster, cheaper, and more transparent system for global financial transactions. The trip will necessitate meticulous preparation, regulatory clarity, and an emphasis on interoperability. While the journey to a CBDC-driven future presents hurdles, the potential benefits for global trade, financial inclusion, and economic growth are apparent.
Final Thoughts
The Ripple CBDC Platform’s capacity for central banks and governments to change their currency plans throughout the CBDC production lifecycle is a fundamental distinction. Adapting CBDC plans to meet the aims of a certain country necessitates this type of adaptable solution and business planning before a pilot begins. As more countries seek to implement CBDC policies, new methods of executing and accelerating cross-border transactions should emerge, allowing central banks to provide value to consumers and businesses.
If you want to kickstart your journey to CBDC implementation and FinTech app development services, contact our FinTech experts at Tntra’s software product engineering company.
Schedule a CALL NOW!





